Exemplary Synchronous Condenser Circuit Diagram

1 1 disadvantage of low power factor.
Synchronous condenser circuit diagram. It can generate or absorb reactive volt ampere var by varying the excitation of its field winding. Two 220 33 kv 75mva transformers with 7 5 short circuit impedance. An ideal load less synchronous motor draws leading current at 90 o electrical.
Two synchronous condensers with 20mva rated power. Synchronous condensor is also known as synchronous compensator or synchronous phase modifier. 320 mva system short circuit power from utility.
The system is not silent since the synchronous motor has to rotate continuously. This characteristics is similar to a normal capacitor which takes leading power factor current. Two 38 mvar pfc system consisting of 4th 5th 7th 11th and 17th harmonic filter units connected to both 33 kv 60hz bus.
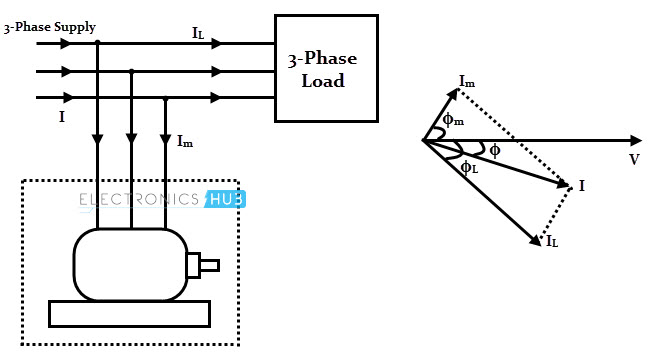
It can be made to take a leading current with over excitation of its field winding. In thefigure v represents the system voltage i is the current drawn from the supply before the addition of power factor correction equipment and cos ϕ is the associated power factor. If a capacitance c is connected in parallel with the load then this will introduce an additional current component i c.
Although synchronous condenser system has some disadvantages. The circuit and phasor diagrams of figure 17 4 illustrate the situation. As the active power provided to motor is 0 at unity p f that means armature current is zero.
This is shown in the phasor diagram fig. The short circuit withstand limit of the armature winding of a synchronous motor is high. This is the property due to which synchronous motor is used as a phase advancer or as.